Metronidazole is an antimicrobial and antiprotozoal drug. It promotes the disruption of DNA synthesis, which causes the death of microorganisms. When taken orally, Metronidazole is quickly and almost completely absorbed (about 80% in 1 hour).
Pharmacotherapeutic group: antimicrobial and antiprotozoal drug
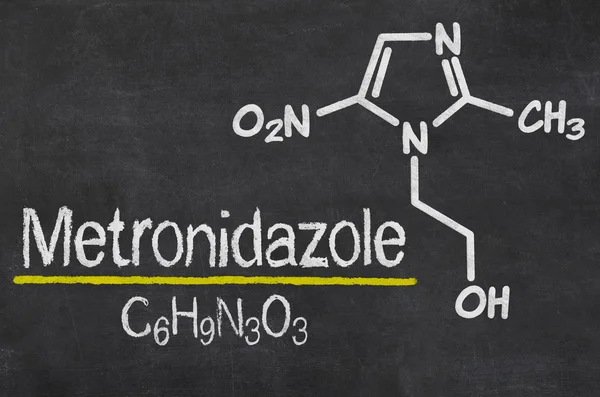
INN: Metronidazole
Indications for use:
Protozoal infections: extraintestinal amebiasis (including amebic liver abscess), intestinal amebiasis (amebic dysentery), trichomoniasis.
Infections caused by Bacteroides spp. (including B. fragilis, B. distasonis, B. ovatus, B.thetaiotaomicron, B. vulgatus); bone and joint infections; infections of the central nervous system (CNS), including meningitis, brain abscess; bacterial endocarditis; pneumonia, empyema and lung abscess; sepsis.
Infections caused by Clostridium spp., Peptococcus niger or Peptostreptococcus spp.: abdominal infections (peritonitis, liver abscess), infections of the pelvic organs (endometritis, abscesses of the fallopian tubes and ovaries, infections of the vaginal vault).
Pseudomembranous colitis associated with the use of antibiotics,
Gastritis or duodenal ulcer associated with Helicobacter pylori (as part of complex therapy).
Prevention of postoperative complications (especially after intestinal, perianal, appendectomy and gynecological operations).
It is available in the form of tablets (250 mg) in packs of 10 or 20 tablets in a contour cell package.
Pharmacological Properties
Pharmacodynamics:
Metronidazole is a derivative of 5-nitroimidazole. The mechanism of action of metronidazole is based on the biochemical restoration of the 5-nitro group of metronidazole inside the cell by transport proteins of anaerobic microorganisms and simplest organisms. The restored 5-nitro group of metronidazole interacts with the cell’s DNA, inhibiting the synthesis of their nucleic acids, leading to the death of microorganisms.
It is active against Trichomonas vaginalis, Entamoeba histolytica, and Gram-negative anaerobes Bacteroides spp. (including B. fragilis, B. ovatus, B. distasonis, B. thetaiotaomicron, B. vulgatus), Fusobacterium spp., and some Gram-positive anaerobes (sensitive strains Eubacterium spp., Clostridium spp., Peptococcus niger, Peptostreptococcus spp.). The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) for these strains is 0.125-6.25 μg/ml. In combination with amoxicillin, it is active against Helicobacter pylori (amoxicillin suppresses the development of resistance to metronidazole).
Metronidazole is not sensitive to aerobic microorganisms and facultative anaerobes, but in the presence of a mixed flora (aerobes and anaerobes) metronidazole acts synergistically with antibiotics effective against ordinary aerobes.
Pharmacokinetics
After oral administration, Metronidazole is rapidly and almost completely absorbed (about 80% in 1 hour). Food intake does not affect the absorption of metronidazole. The bioavailability is not less than 80%. After oral administration of metronidazole in a dose of 500 mg, its concentration in the blood plasma is 10 μg/ml in 1 hour and 13.5 μg/ml in 3 hours. Binding to blood proteins is insignificant and does not exceed 10-20%. Metronidazole quickly penetrates into tissues (lungs, kidneys, liver, skin, bile, cerebrospinal fluid, saliva, seminal fluid, vaginal secretions), into breast milk and passes through the placental barrier. About 30-60% of metronidazole is metabolized by hydroxylation, oxidation and glucuronidation. The main metabolite (2-oximetroneidazole) also has a protozoan and antimicrobial effect.
40-70% of metronidazole is excreted by the kidneys (in unchanged form – about 35% of the total dose). The half-life is 8-10 hours.
In patients with impaired renal function, with a course of metronidazole administration, an increase in its concentration in the blood serum is possible.
Indications for use
Extraintestinal amoebiasis (including amebic liver abscess), intestinal amoebiasis (amebic dysentery), trichomoniasis.
Infections caused by Bacteroides spp. (including B. fragilis, B. distasonis, B. ovatus, B.thetaiotaomicron, B. vulgatus); bone and joint infections; central nervous system (CNS) infections, including meningitis, brain abscess; bacterial endocarditis; pneumonia, empyema and lung abscess; sepsis.
Infections caused by Clostridium spp., Peptococcus niger u Peptostreptococcus spp.: abdominal infections (peritonitis, liver abscess), pelvic organ infections (endometritis, abscesses of the fallopian tubes and ovaries, infection of the vagina vault).
Pseudomembranous colitis associated with the use of antibiotics.
Gastritis or duodenal ulcer associated with Helicobacter pylori (as part of complex therapy).
Prevention of postoperative complications (especially after operations on the large intestine, in the perirectal area, appendectomy, gynecological operations).
Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to metronidazole, to other nitroimidazole derivatives, to imidazoles and to other components of the preparation.
- Organic CNS lesions (including epilepsy).
- Leukopenia (including in the anamnesis).
- Hepatic insufficiency (in the case of appointment of large doses).
- Pregnancy.
- Lactation period.
- Children’s age up to 6 years.
With caution
- Hepatic encephalopathy.
- Acute and chronic diseases of the peripheral and central nervous system (risk of exacerbation of neurological symptoms).
- Renal insufficiency.
Use during pregnancy and while breastfeeding
Since metronidazole passes through the placental barrier and its effect on human fetal organogenesis is unknown, the use of the drug during pregnancy is contraindicated. Metronidazole is excreted into breast milk, so the use of the drug during breastfeeding is contraindicated.
Method of use and dosage
Metronidazole is taken orally, before or after meals, with enough water.
For intestinal amebiasis, metronidazole is given in a daily dose of 1500 mg (divided into 3 doses) for 7 days.
For acute amoebic dysentery, the daily dose is 2250 mg (divided into 3 doses). Children from 6 to 15 years of age are given a daily dose of 500 mg (divided into 2 doses).
For liver abscess and other extra-intestinal forms of amebiasis, the maximum daily dose is 2500 mg (divided into 3 doses) for 3-5 days, in combination with tetracycline antibiotics and other methods of therapy. Children from 6 to 15 years of age are given a daily dose of 500 mg (divided into 2 doses).
For trichomoniasis in women (urethritis and vaginitis) metronidazole is administered once in a dose of 2 g or as a course of treatment, at 250 mg 2 times a day for 10 days.
For trichomoniasis in men (urethritis) metronidazole is administered once in a dose of 2 g or as a course of treatment, at 250 mg 2 times a day for 10 days.
For the treatment of anaerobic infections, treatment is usually started with intravenous infusions, followed by switching to tablets. For adults, the dose of the drug is 500 mg 3 times a day. The duration of treatment is up to 7 days.
For pseudomembranous colitis, metronidazole is prescribed at 500 mg 3-4 times a day. The duration of treatment is determined by the doctor.
For eradication of Helicobacter pylori, metronidazole is prescribed at 500 mg 3 times a day as part of combination therapy (for example, with amoxicillin).
For prevention of postoperative complications, metronidazole is prescribed in a daily dose of 750-1500 (divided into 3 doses) for 3-4 days before surgery. 1-2 days after surgery (when ingestion is already allowed), metronidazole is prescribed at 750 mg per day for 7 days.
Side effect
Gastrointestinal disturbances
- Epigastric pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea.
- Inflammation of the oral mucosa (glossitis, stomatitis), alteration of taste sensations (“metallic” taste in the mouth), decreased appetite, anorexia, dryness of the oral mucosa, constipation.
- Pancreatitis (reversible cases).
- Change in the color of the tongue / “coated” tongue (due to excessive growth of fungal microflora).
Immune system disturbances
- Angioneurotic edema, anaphylactic shock.
Nervous system disturbances
- Peripheral sensory neuropathy.
- Headache, convulsions, dizziness.
- Cases of encephalopathy (e.g., confusion) and subacute encephalomyelitis (disorders of coordination and synergy of movements, ataxia, dysarthria, gait disorders, nystagmus and tremor), which regress after metronidazole withdrawal, were reported.
- Aseptic meningitis.
Psychic disorders
- Psychotic disorders, including confusion, hallucinations.
- Depression, insomnia, irritability, increased excitability.
Vision disturbances
- Transient visual disturbances, such as diplopia, myopia, blurred vision, decreased visual acuity, impaired color perception.
- Neuropathy / neuritis of the optic nerve.
Hearing and labyrinthine disturbances
- Hearing disturbances / hearing loss (including neurosensory deafness).
- Noise in the ears.
Blood and lymphatic system disturbances
- Agranulocytosis, leukopenia, neutropenia and thrombocytopenia.
Liver and biliary tract disturbances
- Increased activity of “liver” enzymes (aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT), alkaline phosphatase), development of cholestatic or mixed hepatitis, hepatocellular liver damage sometimes accompanied by jaundice.
- In patients receiving treatment with metronidazole in combination with other antibiotics, cases of liver failure requiring liver transplantation have been observed.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
- Rash, itching, flushing of the skin, hyperemia of the skin, urticaria. Erythema multiforme.
- Fixed drug eruption.
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis.
Kidney and urinary tract disorders
- Possible discoloration of urine to brownish-red due to the presence in the urine of a water-soluble metabolite of metronidazole.
- Dysuria, polyuria, cystitis, incontinence, candidiasis.
General disorders
- Fever, nasal congestion, arthralgias, weakness.
Laboratory and instrumental data
- Flat T wave on ECG.
Overdose
It has been reported that single doses of metronidazole up to 12 g can be taken in suicidal attempts and accidental overdoses. Symptoms: vomiting, ataxia, mild disorientation. Treatment: there is no specific antidote for an overdose of metronidazole. In case of suspected significant overdosing, symptomatic and supportive therapy should be carried out.
Interaction with other drugs
With disulfiram
It has been reported that psychiatric reactions may occur in patients receiving metronidazole and disulfiram concurrently (a minimum two-week interval between the administration of these drugs is required).
With ethanol
The occurrence of disulfiram-like reactions (skin flushing, skin redness, vomiting, tachycardia) may be possible.
With indirect anticoagulants (warfarin)
The anticoagulant effect may be enhanced and the risk of bleeding due to decreased hepatic metabolism of indirect anticoagulants may be increased, requiring more frequent control of the prothrombin time and, if necessary, adjustment of anticoagulant doses. When administered concurrently with metronidazole, the concentration of lithium, creatinine and electrolytes in the blood plasma should be monitored.
With lithium preparations
Concurrent use of metronidazole may increase the concentration of lithium in the blood plasma. When used concurrently, the concentration of lithium, creatinine and electrolytes in the blood plasma should be monitored.
With cyclosporine
Concurrent use of metronidazole may increase the concentration of cyclosporine in the blood plasma. When used concurrently, the concentration of cyclosporine and creatinine in the blood plasma should be monitored.
With cimetidine
Cimetidine inhibits the metabolism of metronidazole, which can lead to an increased concentration of the latter in the blood serum and an increased risk of side effects.
With drugs inducing microsomal oxidation enzymes in the liver (phenobarbital, phenytoin)Concurrent use of metronidazole with drugs inducing microsomal oxidation enzymes in the liver (phenobarbital, phenytoin) can accelerate the elimination of metronidazole, resulting in a decrease in its concentration in the blood plasma.
With fluorouracil
Metronidazole reduces the clearance of fluorouracil, leading to an increased toxicity.
With busulfan
Metronidazole increases the concentration of busulfan in the blood plasma, which can lead to the development of severe toxicity of busulfan.
With nondepolarizing muscle relaxants (vecuronium bromide)
It is not recommended to use it concurrently with nondepolarizing muscle relaxants (vecuronium bromide).
With sulfonamides
Sulfonamides enhance the antimicrobial effect of metronidazole.
Special instructions
Since simultaneous intake of metronidazole with alcohol (ethanol) may have an effect similar to that of disulfiram (hyperaemia of cutaneous coverings, influx of blood to cutaneous coverings, vomiting, tachycardia), patients should be warned that during and at least one day after the course of treatment they should not take alcoholic drinks or drugs containing ethanol.
It is necessary to carefully weigh indications for long-term use of the drug (more than 10 days) and, in the absence of strict indications, avoid its long-term use. If, in the presence of strict indications (carefully weighing the ratio between the expected effect and the potential risk of complications), the drug is used for a longer period than usually recommended, treatment should be conducted under the control of haematological parameters (especially leukocytes) and adverse reactions, such as peripheral or central neuropathy, manifested by paresthesias, ataxia, dizziness, convulsions, in which case the treatment should be discontinued.
For the treatment of trichomonas vaginitis in women and trichomonas urethritis in men, it is necessary to abstain from sexual intercourse. Simultaneous treatment of sexual partners is mandatory. Treatment does not stop during menstruation. After trichomoniasis therapy, control tests should be carried out during the next 3 cycles before and after menstruation.
Severe hepatotoxicity/acute liver failure (including cases with fatal outcome) have been reported in patients with Coccaine syndrome. Metronidazole should be used with caution and only in the absence of alternative treatment in this group of patients.
Liver function studies should be performed at the beginning, during treatment and for 2 weeks after treatment.
Patients with Coccaine syndrome should be advised to immediately report to the doctor any symptoms of potential liver damage (such as newly detected persistent abdominal pain, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, fever, malaise, jaundice, darkening of urine or skin itching).
It should be noted that metronidazole can immobilize treponemes, leading to a false-positive Nelsen test.
The influence on the ability to operate motor vehicles and mechanisms
Considering the risk of developing such side reactions as confusion of consciousness, dizziness, hallucinations, vision disturbances, it is recommended to refrain from driving a car and engaging in other potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions during treatment.
Form of release
Tablets, 250 mg.
10 or 20 tablets in a contour cell package. 1 or 2 contour packages with instructions for use in a cardboard box.
Storage conditions
Store at a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C.
Store in a place inaccessible to children.
Shelf life
4 years. Do not use after the expiration date stated on the package.
Release conditions
Released by prescription.



No Comments